Introduction
The enterprise network has undergone a significant transformation in the last decade. The traditional data center model, where all applications and services were hosted on premises, is being replaced by cloud-first and hybrid architectures. Businesses today rely heavily on SaaS platforms like Microsoft 365, Salesforce, and Zoom, along with public and private cloud workloads. This shift has created new demands on wide area networks (WANs) that legacy models struggle to meet.
Traditional WAN technologies were designed for predictable, centralized traffic flows, but modern organizations operate in a distributed world with branch offices, remote workers, and multi-cloud environments. The result is that older WAN models often create bottlenecks, increase latency, and add significant costs to IT operations.
Software-Defined Wide Area Networking (SD-WAN) has emerged as a transformative solution to address these challenges. It is not simply a replacement for legacy WANs but a reimagined approach that combines flexibility, cost efficiency, and built-in security while improving network performance.
What Is SD-WAN?
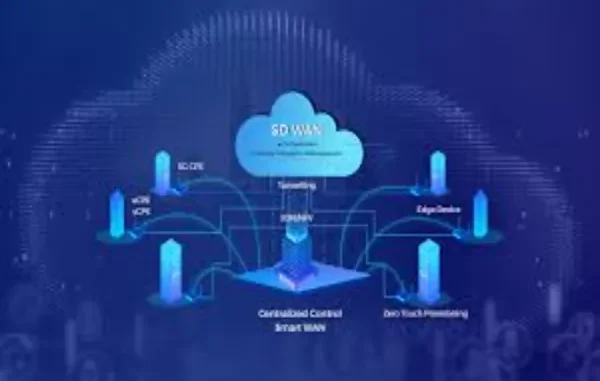
At its core, SD-WAN is a software-defined approach to managing wide area networks. Unlike legacy WANs that relied heavily on expensive MPLS circuits, SD-WAN enables enterprises to use multiple types of connectivity-broadband, LTE, 5G, and MPLS-while intelligently managing traffic between them.
The “software-defined” aspect means the network can be managed centrally through policies, rather than configuring each device individually. This centralization makes SD-WAN more agile and easier to scale. It differs from traditional VPNs and MPLS by providing real-time visibility into application traffic and making intelligent routing decisions based on performance needs.
By combining centralized orchestration, application-aware routing, and security integration, SD-WAN ensures that business-critical applications receive priority and that data moves across the network efficiently. For those who want a deeper breakdown, a detailed guide to SD-WAN technology offers an in-depth look at how it works and why enterprises are rapidly adopting it.
How SD-WAN Works in Practice
To understand SD-WAN in action, it helps to look at its architecture. Centralized orchestration allows IT teams to define policies governing traffic routed across all network locations. This reduces manual configuration and ensures consistency.
Dynamic path selection is another defining feature. Rather than relying on a single MPLS line, SD-WAN evaluates multiple connections, including broadband, LTE, and 5G, in real time. Depending on latency, jitter, or bandwidth conditions, traffic is directed over the best available path.
Application-level visibility allows IT teams to monitor and prioritize traffic based on business needs. For example, video conferencing applications can be prioritized over less critical background updates. At the same time, SD-WAN integrates security measures, ensuring that performance improvements do not come at the cost of increased risk.
Performance Challenges of Legacy WAN Architectures
Legacy WANs are no longer well-suited for today’s cloud-first enterprises. One of the biggest performance issues stems from backhauling traffic through central data centers. While this design made sense when applications were hosted on premises, it adds unnecessary latency when most workloads now live in the cloud.
The high operational cost of MPLS circuits is another major concern. Enterprises often overspend on inflexible bandwidth and cannot scale easily to support growing remote sites or new branches.
Scalability itself is a significant challenge. Expanding to new locations can take weeks or months due to the rigid nature of traditional WAN provisioning. Legacy WANs often deliver inconsistent performance, particularly for SaaS applications, leaving users frustrated and impaired productivity.
How SD-WAN Improves Network Performance
SD-WAN directly addresses these limitations by enabling direct-to-cloud connectivity. Instead of routing traffic through a central hub, users can connect directly to SaaS and IaaS platforms, significantly reducing latency and improving responsiveness.
Intelligent routing ensures that critical applications always receive the bandwidth they need. For instance, VoIP calls and video meetings are prioritized, while non-essential traffic is routed along alternative paths. This prioritization enhances the overall user experience and keeps business-critical services running smoothly.
Bandwidth aggregation allows enterprises to combine multiple internet links, including broadband and wireless connections, into a single pool. This not only improves efficiency but also provides redundancy. Real-time monitoring and automated adjustments ensure optimal performance, even when network conditions change unexpectedly.
Security Advantages That Support Performance
Performance alone is not enough; enterprises also need strong security baked into their WAN. SD-WAN includes features such as end-to-end encryption, ensuring data is secure while moving across the network. Integrated firewalls and intrusion prevention add another layer of protection, reducing reliance on separate security appliances.
Many SD-WAN platforms integrate with Secure Access Service Edge (SASE), combining networking and security into a single, cloud-delivered framework. This allows for consistent security enforcement across distributed environments. Zero Trust access models also ensure that remote users and branch offices connect securely with least-privilege access, minimizing the risk of breaches.
Business Benefits of SD-WAN Adoption
Enterprises that adopt SD-WAN often see immediate cost benefits by replacing or augmenting MPLS with broadband or 5G connections. These alternatives deliver similar or better performance at a fraction of the price.
Improved employee productivity is another key benefit. By ensuring reliable access to cloud applications, SD-WAN reduces downtime and helps teams collaborate more effectively. Greater uptime and resilience are achieved through automatic failover, which seamlessly shifts traffic during outages.
Finally, centralized management simplifies IT operations. Network policies can be deployed once and applied everywhere, reducing complexity for IT teams and accelerating response times to new business requirements.
Industry Use Cases of SD-WAN Performance Gains
In finance, low-latency access to trading and banking applications is critical. SD-WAN ensures that transactions remain secure and fast, even across global networks.
Healthcare organizations use SD-WAN to support telehealth, electronic medical records, and connected devices. Patient data remains safe with strong security and low latency, and doctors can deliver care more effectively.
Retailers rely on SD-WAN to keep point-of-sale systems running smoothly while supporting e-commerce platforms. Consistent uptime helps protect revenue and ensures customer satisfaction.
In manufacturing, SD-WAN supports IoT and IIoT devices that generate massive amounts of real-time data. Businesses can optimize production and predictive maintenance by ensuring stable and efficient connectivity.
Best Practices for Deploying SD-WAN
Enterprises planning an SD-WAN rollout should start with a comprehensive network readiness assessment. This helps identify bandwidth needs, application priorities, and security requirements.
Choosing a provider with strong cloud-native integrations and advanced security features is also essential. Providers that support hybrid and multi-cloud environments can deliver greater flexibility as businesses scale.
A phased rollout is often the best approach, starting with select locations before expanding enterprise-wide. Continuous monitoring and performance optimization ensure the network aligns with evolving business goals.
The Future of SD-WAN Performance Enhancements
The future of SD-WAN lies in further automation and intelligence. AI-driven optimization will enable networks to predict traffic demands and adjust proactively. Integration with 5G and edge computing will extend SD-WAN’s value to environments where speed and low latency are critical.
Autonomous networking models are also on the horizon, where human intervention is minimal, and networks self-manage based on real-time conditions. This evolution positions SD-WAN as a cornerstone of enterprise digital transformation.
Conclusion
SD-WAN is more than a replacement for traditional WAN technologies. It catalyzes modern enterprise performance, offering agility, security, and cost efficiency. By addressing the challenges of legacy architectures and optimizing access to cloud workloads, SD-WAN empowers businesses to operate at peak efficiency.
As enterprises continue their digital transformation, adopting SD-WAN is not just a technical decision but a strategic one. It is the key to delivering consistent performance, improving productivity, and enabling long-term growth.
FAQs
How is SD-WAN different from traditional WAN solutions?
SD-WAN offers centralized control, intelligent routing, and direct-to-cloud connectivity, while legacy WANs rely on expensive MPLS circuits and centralized backhauling.
Can SD-WAN fully replace MPLS for enterprise networks?
In many cases, yes. SD-WAN can replace MPLS by using broadband, LTE, and 5G. However, some enterprises may adopt hybrid models depending on performance or compliance requirements.
How does SD-WAN improve SaaS and cloud application performance?
By providing direct-to-cloud connectivity and intelligent routing, SD-WAN reduces latency and ensures that business-critical applications are prioritized for optimal performance.
Leave a Reply